The external genital organs have three main functions: It is a mostly cartilaginous structure, with the lobule being the only part not supported by cartilage.
Digestive System The Snapping Turtle Resource
A few of them are explained in detail below.
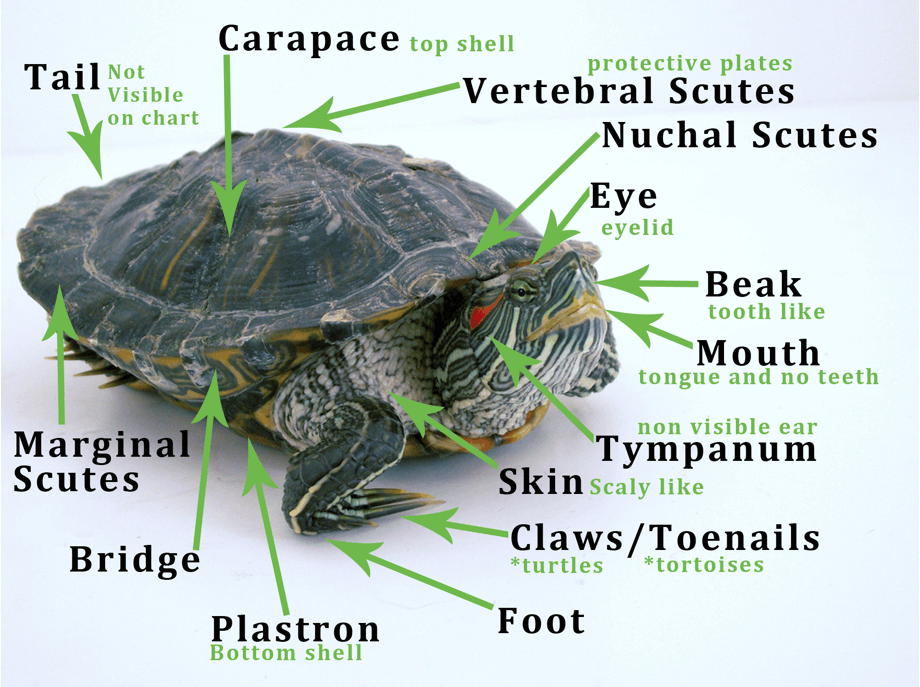
External organs of turtle and their functions. It also holds the parts of the plant up. Transportation of sperms prostate and The area containing these organs is called the vulva.
Production of sperms and male hormones epididymis: Skin is the largest external organ of the human body. Below the shoulders lies the chest, stomach, waist, back and hips.
The food passes through the digestive system, where nutrients are extracted. Human body is an educational science lesson for kids. It is made up of a sac that we call the “pericardium”, in charge of giving flexibility and mobility to this muscle.
They also take in the water and minerals. These organs are macroscopic and are involved in multiple functions. The most obvious function of the integumentary system is to protect animals from the hazards of their environment, but it's also indispensable for temperature regulation (a coating of hair or feathers helps to preserve internal body heat), protection from predators (the thick shell of a turtle makes it a tough snack for crocodiles), sensing.
In such cases the front portion of the fish is called spiny dorsal and the rear portion is called soft dorsal. Suppose to pick up a fallen pencil, we need to bend at our waist to pick up the pencil from the floor. The brain, heart, lungs, liver, kidneys are a few examples of organs.
The flower helps attract insects and birds. These organs are macroscopic in structure. The cartilaginous part of the auricle forms an outer curvature, known as the helix.a second innermost curvature runs in.
The latter consists of three layers: Either of two spongy, saclike respiratory organs in most vertebrates, occupying the chest cavity together with the heart and functioning to remove carbon dioxide from the blood and provide it with oxygen. Passage for semen and urine scrotum:
We can bend in front, sideways and little at the back. The roots hold the plant in the soil. Each part of a plant helps the plant survive and reproduce.
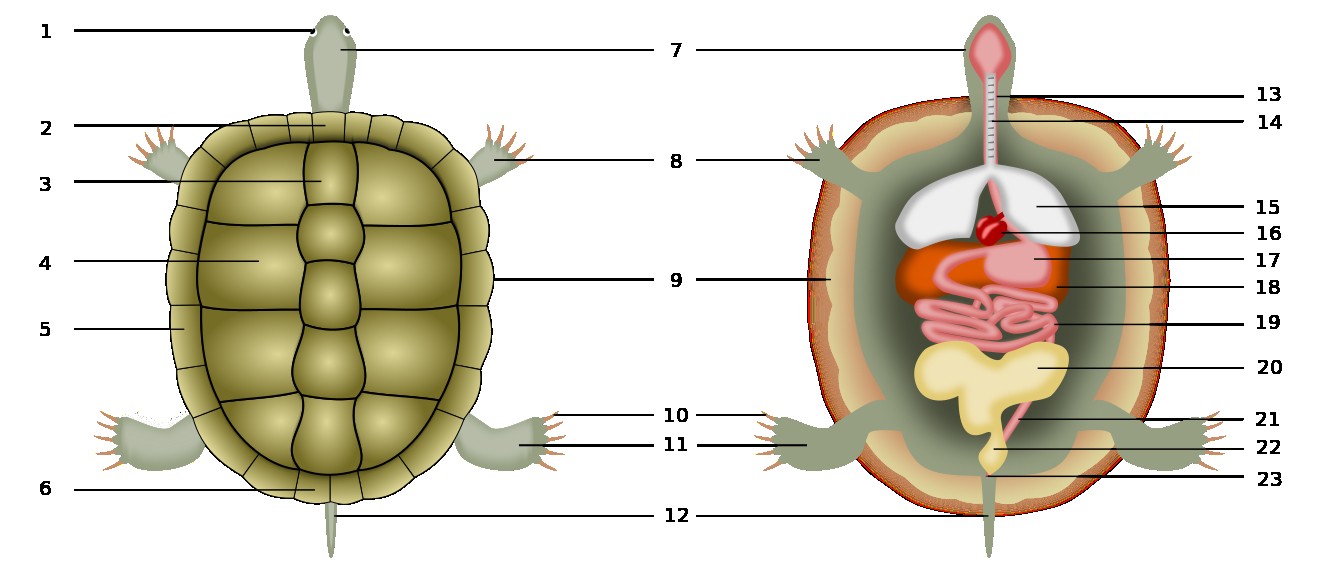
The anatomy of the sea turtle is unique in that it is one of the few creatures to have both an internal and external skeleton. Through simple animation, kids will learn about the different body systems, the skeleton and bones. In turn, the pericardium is divided into a fibrous and a serious part.
The legs are used for locomotion like walking, running, jumping, and swimming. The neck rests on the shoulders. In all species except the leatherback, the external skeleton, whose main purpose is to provide protection and support for internal organs, is comprised of a bony shell which is, itself, divided into two halves:
Morphology in biology the subject dealing with the construction and function of creature's body parts is referred to as morphology. Let’s hold a pencil with our fingers. The auricle is a paired structure found on either side of the head.it functions to capture and direct sound waves towards the external acoustic meatus.
External body parts, sense organs and their functions || class 3, 4 evs#class4evslearningnotebook #class4evs #evsclass4 #bodypartsname #bodyparts#class3evsl. In our body, there are a huge number of organs, the internal organs perform the work, while the external organs link the outside to the inside, for instance, the digestive system organ systems digest the nutrition, but it is the mouth which absorbs in food and the. Some fins are jointed and some are separated at the edge.
The lesson will be followed by several practice exercises. Turtles don't have teeth but a beak for gripping and tearing and keratin plates to help compress their food. The external organs in the female reproductive system are collectively termed, vulva consisting of labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, vaginal orifice, vestibular gland, and hymen.
The body opening through which an animal takes in food. Reservoir and maturation of sperms vas deferens: Food is taken in through the mouth and passed into the gullet.
Different animals use their body parts in different ways to see, hear, grasp objects, protect themselves, move from place to place, and seek, find, and take in food, water and air. On the outside, our bodies are separated into the following obvious parts, head, torso, arms, and legs. Altogether, there are 10 large organs in the body, which include skin, liver, brain, lungs, heart, kidney, spleen, pancreas, thyroid and joints.
Plants also have different parts (roots, stems, leaves, flowers, fruits) that help them survive, grow, and produce more plants. They will learn about organs like the brain, heart, lungs and kidneys; The epicardium, the myocardium, and the endocardium.
Fins act as the organ of locomotion. Fishes that have rays which are bony, stiff, and separated are called spines. The stem carries the water to different parts of the plant.
Labia majors these are large muscular folds surrounding the vulva, comprised of akin, fibrous tissue, fat, and a large number of sebaceous glands. The turtle's internal organs function much like a human's. The leaves make the food for the plant.
Each major part has a specific function. Fins are made up of rigid rays. They are used to make sure that the right levels of salts and sugars.
The main function of the external structure is for receiving sperm during intercourse and providing a covering for internal reproductive organs for their protection. In general, like on this page, morphology can be divided into external morphology (the external appearance) and internal morphology (the construction of organs and organ systems). The external genital organs include the mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, bartholin glands, and clitoris.
The lower plastron and the upper carapace. Maintenance of testicular temperature for proper spermatogenesis:
Turtle Dissection Circulatory system YouTube